Written by Jiri Walek
Have you ever heard about digital tool chain managers? Very likely not. Although we have seen an increasing number of people who work at this position over the past years, this role has not yet been formally defined.
In this article, we aim to shed some light into the role and also explain why Newired often dialogues with digital toolchain managers. We will also explain what our solution can offer to them.
What is a Digital Toolchain
Let’s speak about digital toolchain first …
In software, a toolchain is a set of programming tools which is used to perform a complex task or to create a software product. In general, the tools forming a toolchain are executed consecutively, so the output or resulting environment state of each tool becomes the input or starting environment for the next one. However, the term is also used when referring to a set of related tools which are not necessarily executed consecutively.
Industry 4.0 has changed product manufacturing. At a high level, it represents the vision of the interconnected factory where all equipment is online, and in some way is also intelligent and capable of making its own decisions.
The explosion in connected devices and platforms, combined with the abundance of data from field devices and the rapidly changing technology landscape, has made it imperative for companies to quickly adapt their products and services and move from the physical world to a digital one.
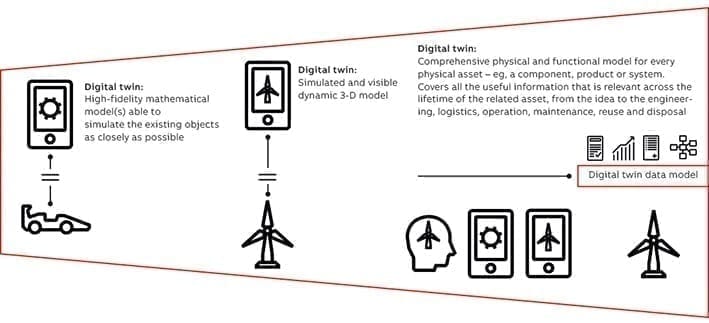
Another direction of this digitalization is the concept of digital twin. Quite simply, a digital twin is a virtual model of a process, product or service. This pairing of the virtual and physical worlds allows for the analysis of data and monitoring of systems to head off problems before they even occur, prevent downtime, develop new opportunities and even plan for the future by using simulations.
Manufacturers are already extending the digital twin strategy across the value chain and making organizational changes to concretise the full potential of digitalization across the entire value chain. They are also taking action to educate their workforce on digital manufacturing and designing technologies.
Who is a Digital Toolchain Manager
Take as an example the growing complexity coming with the electrification of vehicles, autonomous driving and active safety systems. The use of model-based development has emerged as a core enabler for the digital transformation of processes and organizations, using models to formalize the relationship between the different stakeholders of complex engineering projects.
The current trend brings about the challenge of understanding SW tools and applications beyond an IT point of view. The tool selection in the tool chain is increasingly more complex:
- It starts with a proper definition of the digital use case;
- It involves modeling high-level user scenarios which span over the full tool chain and their decomposition into low-level or tool-level use cases;
- It requires the Identification of integration points;
- It includes planning and roadmapping of the transformation over months or years.
Toolchain has now also become more strategic, requiring a higher level of abstraction to succeed with the introduction or extensive adoption of SW tools & application.
As a result, the digital toolchain manager is no longer responsible for the IT site of the toolchain only (In short words – for running it reliably and delivering what the user is asking for), but they manage various disciplines. They:
- Understand and/or manage the definition & update of the production process;
- Manage the solution architecture and the roadmap to cover the production processes with the selected toolchain;
- Plan initiatives to guarantee that the organization (and their users) will follow the new digital process towards business success.
So today we see program managers bearing the duty of launching a successful toolchain and software adoption, or advanced IT managers collaborating with business on needs/values prior to the actual project implementation. In both cases, we see a merged role: that is the Digital Toolchain Manager.
Newired for Digital Toolchain Managers
The last bullet point above,
Plan initiatives to guarantee that the organization (and their users) will follow the new digital process towards business success.
leads towards the reasons why we quite often interact with digital toolchain managers. To ensure that the investment into digital toolchain pays back in time with better competitive advantage and higher effectivity, the organization has to ensure a high level of employee / user satisfaction while performing new workflows.
User satisfaction often depends on several factors:
- Education – The user understands and realizes the value of your digital toolchain and workflows;
- Onboarding – The user is guided through activities that they now need to perform, as simply as possible and with no friction;
- Proficiency – The user becomes proficient and fully embedded in the value the toolchain offers;
- Retention – The user stays educated and proficient over time so he/his effectivity actually grows with time;
With Newired, you can embed a user experience layer to your digital toolchain, so that the users receive step-by-step guidance and contextual help any time they want or need it. This is so not only during the initial educative phase, but during the full toolchain lifecycle.
Newired’s main benefits can be well associated with following diagram representing Newired Learning Curve.
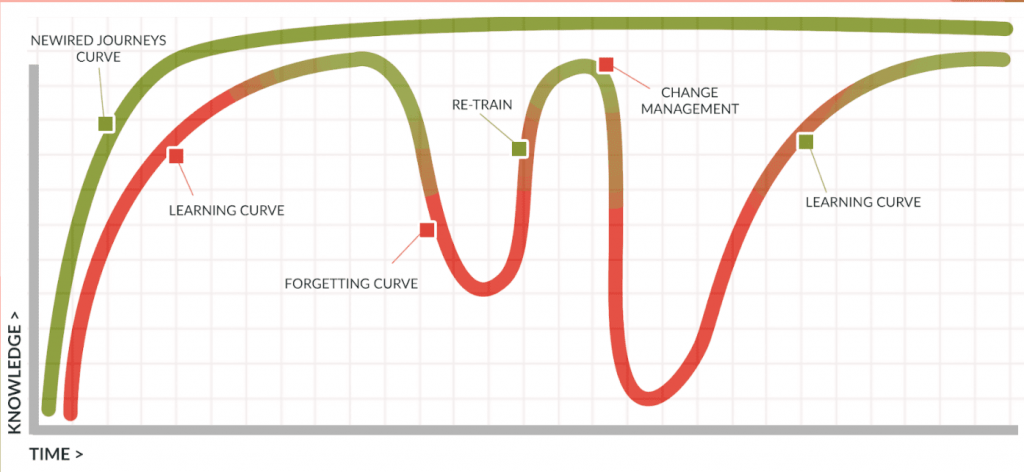
Steep initial learning curve
Learning is embedded in the application: users learn by doing.
The application usability improves, bringing in intuitiveness and reducing the need for guidance.
Knowledge retention – Eliminate the forgetting curve
Users can get guidance any time they need it, directly from application.
Newired offers real-data reporting, to quickly spot bottlenecks and turn them into better user interactions.
Embrace Change – Introduce changes without losing knowledge
Newired allows you to introduce application and process changes in a controlled way, increasing change adoption
With Newired, you can reduce errors and interruptions caused by users who are unaware of the implemented changes.
Contact us if you would like to know how Newired can add value and efficiency to your Digital toolchain!